 Maps
Maps
See also: Results View, Regions, MapWinGIS, Geographic Mapping
Introduction
In addition to using charts and tables to display results, you can also optionally display LEAP results on maps. Using maps in LEAP also requires that you separately install MapWinGIS.
Maps in LEAP share most of the same controls for selecting results as other chart types including the Tree on the left of the screen, the units selection boxes immediately to the left of the map and the tool bars used to select the type of results to be displayed. The Map screen is divided into 3 parts.
-
The main map is displayed on the left of the screen. Use the zoom control at the top left of the map to zoom in and out of the map or select a rectangular shape on the map to zoom to that extent. Alternatively, use the small locator map to the right to navigate. You can also use the pan button (
 ) to switch between selection mode and panning mode in the map. Most options are also accessible by right-clicking on the map.
) to switch between selection mode and panning mode in the map. Most options are also accessible by right-clicking on the map. -
The legend shown on the top-right part of the screen indicates the values associated with each color used on the map.
-
The locator shown on the bottom-right part of the screen gives you a birds-eye view of the full extent of the map. A box drawn on the locator map indicates the part of the map that is currently selected. As you zoom-in or zoom-out of the map, the locator box will be redrawn.
Regional Maps and Gridded Maps
Maps in Results View are available in two circumstances:
- Region Maps: In multi-region areas only, regional results can be displayed on a map with each region corresponding to one shape on the map. Regional results can be shown using three types of maps: gradient maps, bar chart maps and pie chart maps. Gradient maps show results by color coding each map shape. The bar chart maps and pie chart maps show multiple small bar and pie charts on a map, with each small chart centered on a region and with each individual chart showing time series data. These three types of maps require no additional data beyond mapping your regions to shapes in your chosen shape file. The shape file is chosen on the Mapping tab of the General: Settings screen. Regions are mapped to shapes in the General: Regions screen. With gradient maps, the legend shown to the right of the map shows the range of values contained within each category. Gradient maps can be shown using different categories. Click the categories button below the legend to select among different categorizations. The categorization methods available are:
- Natural Breaks: The position of breaks are chosen to minimize the sum of square deviations within categories. The algorithm is heuristic, therefore gives only an approximation of the real position of natural breaks, but typically is recommended as suitable in most cases.
- Unique Values: A category will be created for each unique value of the field. In most circumstances, this will mean that each region is in a separate category.
- Equal Intervals: Each category spans an equal range.
- Equal Count: Each category contains a (roughly) equal number of regions.
- Standard Deviation: Six categories are created, with the range of each of them equal to the standard deviation of the values. Three categories hold values greater than the mean and three lower than it.
Examples of gradient and bar chart maps are shown below:
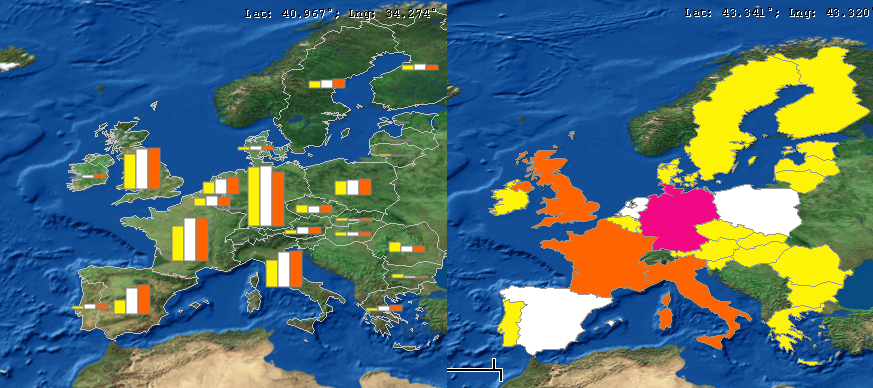
Two examples of the bar and gradient map chart types in LEAP, showing results for each region in a European model.
- Gridded Maps: In both single and multi-region areas, selected energy and environmental loading results can be displayed on a Gridded Map. Displaying this type of map requires three additional steps. (1) First, enable the Map Results to Grid option on the Scope & Scale tab of the General: Settings screen; (2) Next, load a series of proxy GIS data sets into LEAP describing a range of socioeconomic variables that are used to allocate energy use and emissions to the map's grid squares (for example a population map might be used to allocate household energy use to map grid squares). You can set up these proxy GIS data sets using the General: Geographic Mapping screen. (3) Finally, use the Geography variable to allocate energy use and emissions from each LEAP branch to the map's grid squares. Once you have taken these three steps, the additional Gridded Map chart type will be available in Results View via the Map chart type button (
 ) . An example of a gridded map chart type is shown here.
) . An example of a gridded map chart type is shown here.
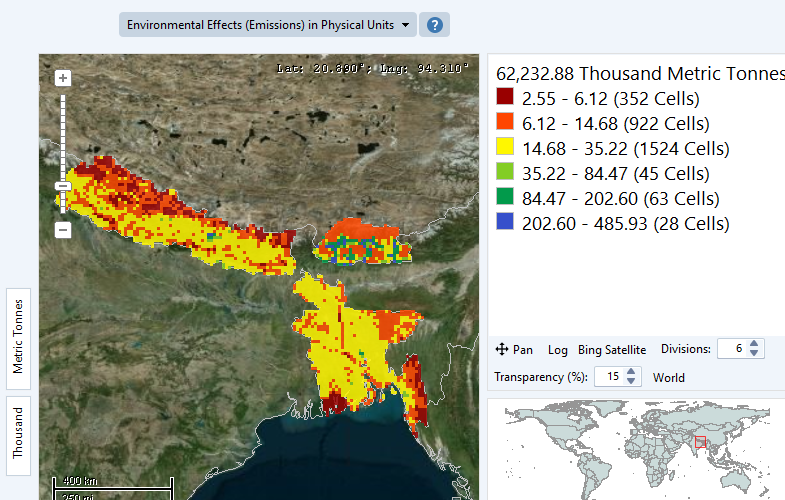
An example of the gridded map chart type.
When viewing gridded maps, it can be particularly useful to use the Split screen view which shows both a map and a table containing all the gridded values in the map. The table is color coded so that values are shown with the same colors as in the map. You can navigate among the table values by holding down the control key while hovering over the map. The table will then automatically scroll to show the value corresponding to the map grid square pointed to by the mouse cursor. You can also show an additional chart next to the table, which shows the time trends in each scenario for the highlighted grid square. Below, we show an example of using the split screen to view a gridded map and to zoom in on the trends for a particular map square.
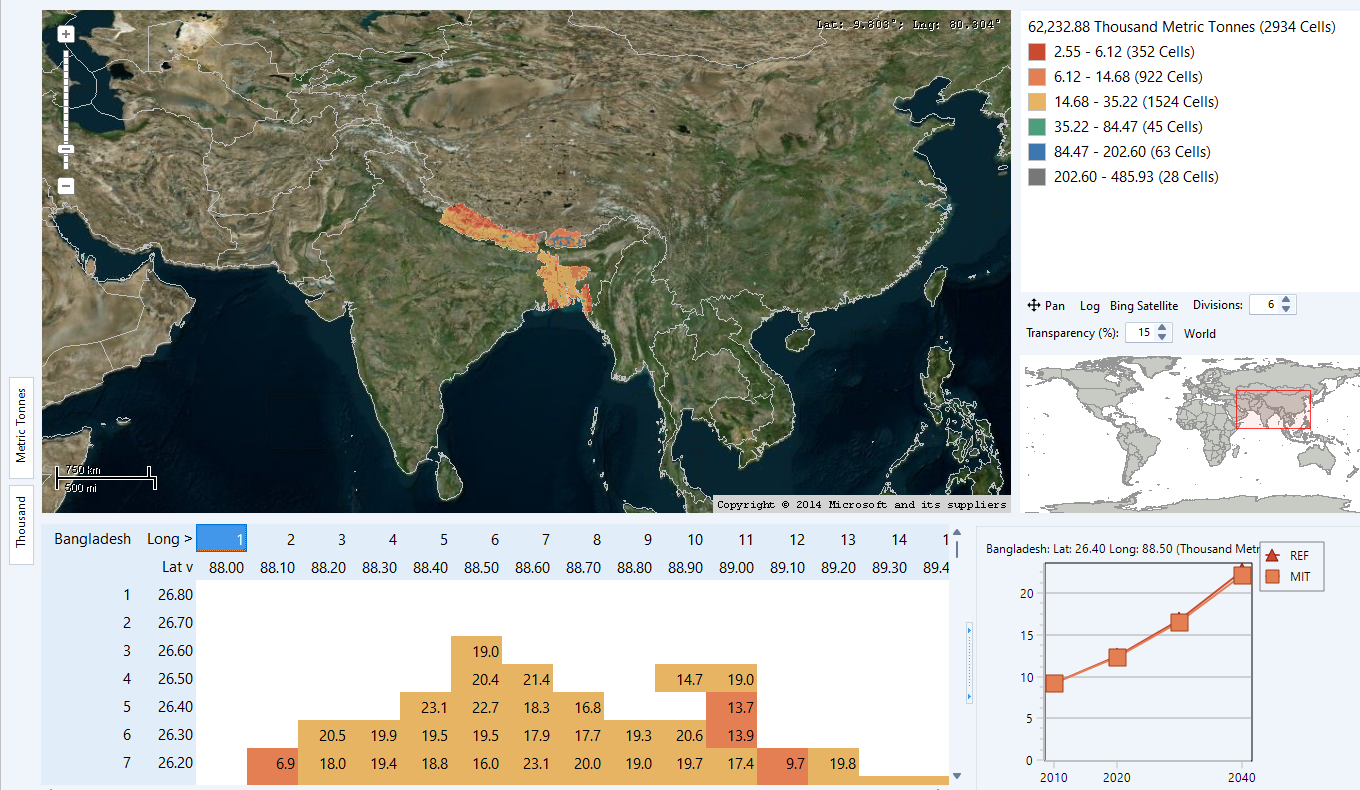
Using the split screen view with a gridded map to zoom in on the trends for a particular map square.
Map Formatting Options
The main options used to control the look of the map are collected on the tool bar shown below the legend. The map options include:
 Pan: use the pan button to switch between two modes for the mouse cursor: panning around the map or selecting a region of the map.
Pan: use the pan button to switch between two modes for the mouse cursor: panning around the map or selecting a region of the map.- Image: Select an internet tile service to provide a background image for the map. The tile services supported are Bing and Open Maps. You can also opt to display a static background image or no background. To use a static background image, first select it on the Mapping tab of the General: Settings screen.
- Divisions: Select the number of value divisions on the map. Each division corresponds to an item in the map legend. You can also select the algorithm used for calculating the division intervals. Division options include: linear, equal count, log and reverse log.
- Chart Size: Use this spin edit to adjust the size of bar and pie charts displayed on a map. The default is 100%. Only relevant for maps with bar and pie charts.
- No Collisions: Use this check box to adjust whether overlapping (colliding) charts will be drawn on the map. Only relevant for maps with bar and pie charts.
- Transparency: Set the transparency of the chart layer from 0-100% so that the background image can be partially viewed through the mapped results.