The View Bar
See also: Main Menu , Main Toolbar
LEAP is structured as a set of different "views" of an energy system. These are listed as graphical icons on the "View Bar", normally located on the left of the screen. Click an icon in the View Bar to select one of the views. In some cases, the system may need to calculate scenarios before the view is displayed. If you are working on a low resolution screen, we suggest that you hide the View Bar to make more space on the screen. Use the menu option View: View Bar to do this. Thereafter, you will need to use the View menu or the mini View toolbar to select different views. Different views can also be accessed via their shortcut keys.
 The Analysis View (Ctrl+Alt+A) is the place where you create your data structures, models, scenarios, and assumptions. In the Analysis view, the screen is divided into three panes. On the left, a hierarchical tree is used to create and organize data structures under major categories such as Key Assumptions, Demand, Transformation, Resources, Non-Energy and Indicators. The tree is also used to select the data to be edited, which is shown on the right of the screen. For example, clicking on the "Electricity Generation" tree branch on the left of the screen, will display the data for that module on the right of the screen. On the top-right of the screen, a data entry table is used to edit data and create modeling relationships. The information you enter here including data values and modeling equations is processed and then displayed the bottom-right pane as charts and tables. The bottom pane also provide a tool that elaborates the relationships between variables in your model (
The Analysis View (Ctrl+Alt+A) is the place where you create your data structures, models, scenarios, and assumptions. In the Analysis view, the screen is divided into three panes. On the left, a hierarchical tree is used to create and organize data structures under major categories such as Key Assumptions, Demand, Transformation, Resources, Non-Energy and Indicators. The tree is also used to select the data to be edited, which is shown on the right of the screen. For example, clicking on the "Electricity Generation" tree branch on the left of the screen, will display the data for that module on the right of the screen. On the top-right of the screen, a data entry table is used to edit data and create modeling relationships. The information you enter here including data values and modeling equations is processed and then displayed the bottom-right pane as charts and tables. The bottom pane also provide a tool that elaborates the relationships between variables in your model ( ) and also provides a place to enter notes.
) and also provides a place to enter notes.
 The Results View (Ctrl+Alt+R) displays detailed results for all parts of the system. It can be used to create a wide variety of charts, tables and maps. Reports can be viewed for one or more scenarios and regions and can be customized in a wide variety of ways. For example it includes tools to help you compare scenarios. You can also use the "Favorites" option to bookmark the most useful charts for your analysis so that you can quickly display them. These favorite charts can later be viewed together in the Overviews view.
The Results View (Ctrl+Alt+R) displays detailed results for all parts of the system. It can be used to create a wide variety of charts, tables and maps. Reports can be viewed for one or more scenarios and regions and can be customized in a wide variety of ways. For example it includes tools to help you compare scenarios. You can also use the "Favorites" option to bookmark the most useful charts for your analysis so that you can quickly display them. These favorite charts can later be viewed together in the Overviews view.
 The Energy Balance View (Ctrl+Alt+E) displays the results of your calculations as a standard energy balance table. Energy balances can be viewed for any year of any calculated scenario or region and can also be customized for example to display levels of detail, or to show different layouts (for example with columns showing fuels, fuel groups or years) or to use different energy units.
The Energy Balance View (Ctrl+Alt+E) displays the results of your calculations as a standard energy balance table. Energy balances can be viewed for any year of any calculated scenario or region and can also be customized for example to display levels of detail, or to show different layouts (for example with columns showing fuels, fuel groups or years) or to use different energy units.
 Sankey diagrams (Ctrl+Alt+S) are a type of flow diagram made of nodes connected by links, in which the width of the links is shown proportional to the energy flow being represented. Sankey Diagrams in LEAP are are a representation of the energy flows in a standard energy balance. They give an overview of energy flows through an area from primary resources through the conversion in each transformation module to their consumption in final energy demand sectors. Sankey diagrams also include a representation of such details as imports, exports, stock changes, statistical differences and losses. You can display a Sankey diagram for any year of any scenario. In multi-region areas you can show the Sankey diagram for the whole area or for any particular region.
Sankey diagrams (Ctrl+Alt+S) are a type of flow diagram made of nodes connected by links, in which the width of the links is shown proportional to the energy flow being represented. Sankey Diagrams in LEAP are are a representation of the energy flows in a standard energy balance. They give an overview of energy flows through an area from primary resources through the conversion in each transformation module to their consumption in final energy demand sectors. Sankey diagrams also include a representation of such details as imports, exports, stock changes, statistical differences and losses. You can display a Sankey diagram for any year of any scenario. In multi-region areas you can show the Sankey diagram for the whole area or for any particular region.
 The Cost-Benefit Summary (Ctrl+Alt+C) is a specialized report summarizing the overall costs and benefits of one scenario versus another. Typically, you would use it to display the overall Net Present Value (NPV) of one or more policy scenarios versus a baseline scenario. The report shows cumulative discounted costs over all the years in a scenario, noting the differences in costs in each different sector and also show the total for each scenario as whole (i.e. the NPV).
The Cost-Benefit Summary (Ctrl+Alt+C) is a specialized report summarizing the overall costs and benefits of one scenario versus another. Typically, you would use it to display the overall Net Present Value (NPV) of one or more policy scenarios versus a baseline scenario. The report shows cumulative discounted costs over all the years in a scenario, noting the differences in costs in each different sector and also show the total for each scenario as whole (i.e. the NPV).
 Affordability Analyses are used to examine the costs to consumers of different scenarios and how they compare to the incomes of those consumers (or the revenues of industrial consumers). The affordability of scenarios can be a good indicator of their achievability, and can also be important in helping to understand if pathways meet environmental social justice goals.
Affordability Analyses are used to examine the costs to consumers of different scenarios and how they compare to the incomes of those consumers (or the revenues of industrial consumers). The affordability of scenarios can be a good indicator of their achievability, and can also be important in helping to understand if pathways meet environmental social justice goals.
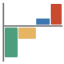 Marginal Abatement Cost Curves (MACCs) (Ctrl+Alt+M) assess the relative cost and abatement potential of each different mitigation option, plotted in ascending order of cost. MACCs plot cumulative emissions reductions from successive mitigation options (e.g. tonnes of GHGs avoided in CO2e) against the incremental cost per unit of emission reduction (e.g. $/T CO2e). A key property of a MACC is that, for any given set of options the area enclosed by the options in the MACC chart equals the cumulative avoided cost of those options. A MACC makes it easy to see which options are low or negative cost (negative cost options appear below the X axis) and which options have the largest mitigation potential (those with the widest bars).
Marginal Abatement Cost Curves (MACCs) (Ctrl+Alt+M) assess the relative cost and abatement potential of each different mitigation option, plotted in ascending order of cost. MACCs plot cumulative emissions reductions from successive mitigation options (e.g. tonnes of GHGs avoided in CO2e) against the incremental cost per unit of emission reduction (e.g. $/T CO2e). A key property of a MACC is that, for any given set of options the area enclosed by the options in the MACC chart equals the cumulative avoided cost of those options. A MACC makes it easy to see which options are low or negative cost (negative cost options appear below the X axis) and which options have the largest mitigation potential (those with the widest bars).
 Decomposition Reports (Ctrl+Alt+T) help you analyze the factors underlying the trends in your scenarios using decomposition reports. They draw upon the methodologies known as IPAT and the Kaya identity, with results typically plotted as "waterfall" charts to help you see the progression of different factors that impact on your pathways.
Decomposition Reports (Ctrl+Alt+T) help you analyze the factors underlying the trends in your scenarios using decomposition reports. They draw upon the methodologies known as IPAT and the Kaya identity, with results typically plotted as "waterfall" charts to help you see the progression of different factors that impact on your pathways.
 The Overviews View (Ctrl+Alt+O) is used to group together "Favorite" charts created earlier in the Results view. With Overviews, you get a birds-eye view of different important aspects of the energy system, such as costs, environmental impacts, and resource requirements. You can create multiple named Overviews, each of which can display up to 10 different Favorites.
The Overviews View (Ctrl+Alt+O) is used to group together "Favorite" charts created earlier in the Results view. With Overviews, you get a birds-eye view of different important aspects of the energy system, such as costs, environmental impacts, and resource requirements. You can create multiple named Overviews, each of which can display up to 10 different Favorites.
 TED: The Technology and Environmental Database (Ctrl+Alt+T) provides extensive information describing the technical characteristics, costs and environmental impacts of a wide range of energy technologies available internationally or in particular developing country regions. The database includes information on existing technologies, current best practices and next generation devices. TED includes data on approximately one thousand technologies, referencing reports by dozens of institutions such as the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change , the U.S. Department of Energy, and the International Energy Agency, as well as data specific to energy technologies found in developing countries.
TED: The Technology and Environmental Database (Ctrl+Alt+T) provides extensive information describing the technical characteristics, costs and environmental impacts of a wide range of energy technologies available internationally or in particular developing country regions. The database includes information on existing technologies, current best practices and next generation devices. TED includes data on approximately one thousand technologies, referencing reports by dozens of institutions such as the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change , the U.S. Department of Energy, and the International Energy Agency, as well as data specific to energy technologies found in developing countries.
 The Notes View (Ctrl+Alt+N) is a word processing tool with which you can enter documentation and references for each branch of the tree. Notes can include formatting (bold, underline, italics, etc.) and can also include embedded images and links to documents on the internet. The editor includes standard word processing options such as the ability to add bulleted (
The Notes View (Ctrl+Alt+N) is a word processing tool with which you can enter documentation and references for each branch of the tree. Notes can include formatting (bold, underline, italics, etc.) and can also include embedded images and links to documents on the internet. The editor includes standard word processing options such as the ability to add bulleted ( ) or numbered (
) or numbered ( ) lists, change text alignment (
) lists, change text alignment (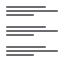 /
/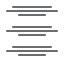 /
/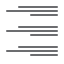 /
/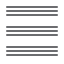 ) and to indent or unindent paragraphs (
) and to indent or unindent paragraphs ( /
/ ).
).